project management · Aug 8, 2024
What is Project Life Cycle? The 5 Project Phases and Management Steps

The project life cycle serves as the foundational framework for guiding projects from conception to completion. Understanding the project life cycle is crucial for project managers and teams to ensure successful project delivery, efficient resource management, and achievement of project goals.
This blog post delves into what the project life cycle entails, explores the five distinct phases of a project, outlines the benefits of adhering to this structured approach, and provides insights into managing the project life cycle using modern tools like Quire. Finally, we'll address frequently asked questions about the project life cycle.
What is the Project Life Cycle?
The project life cycle is a structured sequence of phases a project goes through from initiation to closure. Each phase represents a distinct stage in the project’s development, characterized by specific deliverables, tasks, and objectives. The primary purpose of the project life cycle is to provide a clear roadmap that guides project teams in managing activities, resources, and risks effectively.
A well-defined project life cycle ensures that the project progresses in an organized manner, with each phase building upon the previous one. This structured approach not only facilitates better planning and execution but also enables stakeholders to monitor progress, identify potential issues early, and make informed decisions.
What are the Project Phases?
The project life cycle comprises five main phases: Initiation, Planning, Execution, Monitoring and Controlling, and Closure. Each phase serves a specific purpose and involves unique activities and deliverables.
- Project Initiation Phase
- Project Planning Phase
- Project Execution Phase
- Project Monitoring and Controlling Phase
- Project Closure Phase
Project Initiation Phase
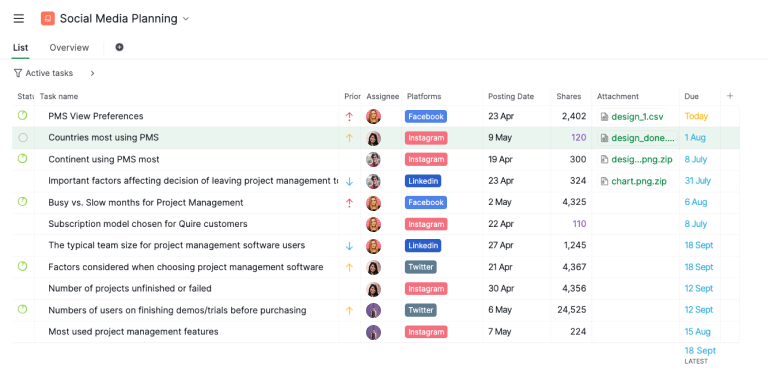
The Project Initiation Phase is the first step in the project life cycle, where the project's objectives, scope, purpose, and feasibility are defined. During this phase, key activities include developing a project charter, identifying stakeholders, and gathering initial requirements.
The goal is to establish a clear understanding of what the project aims to achieve and secure the necessary approvals and resources to move forward. This phase sets the foundation for the entire project, ensuring alignment among stakeholders and laying out a roadmap for subsequent planning and execution.
- Defining the Project Scope: Clearly outline the project's objectives, goals, and constraints.
- Feasibility Study: Analyze to determine the project's viability, including cost-benefit analysis and risk assessment.
- Stakeholder Identification: Identify all stakeholders, including sponsors, team members, and end-users.
- Project Charter: Develop a project charter that formally authorizes the project, detailing the scope, objectives, stakeholders, and key deliverables.
- Initial Resource Allocation: Estimate and allocate initial resources required for the project's initiation.
Project Planning Phase
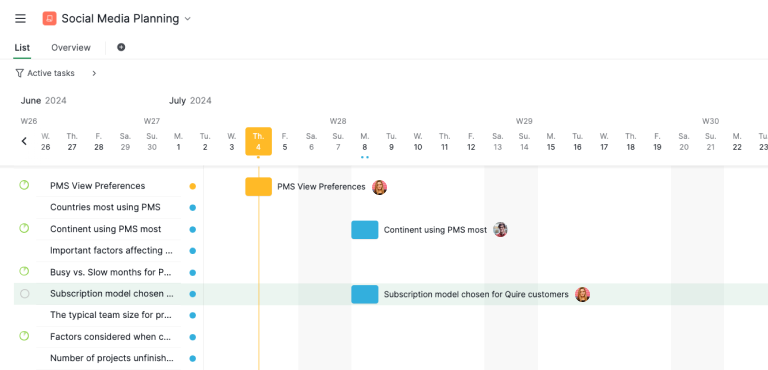
The Project Planning Phase is a critical stage in the project life cycle where detailed plans are developed to guide the project's execution. This phase involves defining the project's scope, objectives, and deliverables in detail, creating schedules, allocating resources, and setting up communication channels.
Key activities include risk assessment, budgeting, and establishing performance metrics. The goal is to create a comprehensive plan that outlines how the project will be managed and executed, ensuring all team members and stakeholders are aligned and prepared for the tasks ahead. Effective planning sets the foundation for project success by providing a clear roadmap and anticipating potential challenges.
- Developing the Project Plan: Create a comprehensive project plan outlining tasks, timelines, resources, and budget.
- Risk Management Planning: Identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies.
- Resource Planning: Allocate resources, including team members, equipment, and budget.
- Communication Plan: Establish a communication plan to ensure effective information flow among stakeholders.
- Quality Planning: Define quality standards and processes to ensure project deliverables meet the required criteria.
Project Execution Phase
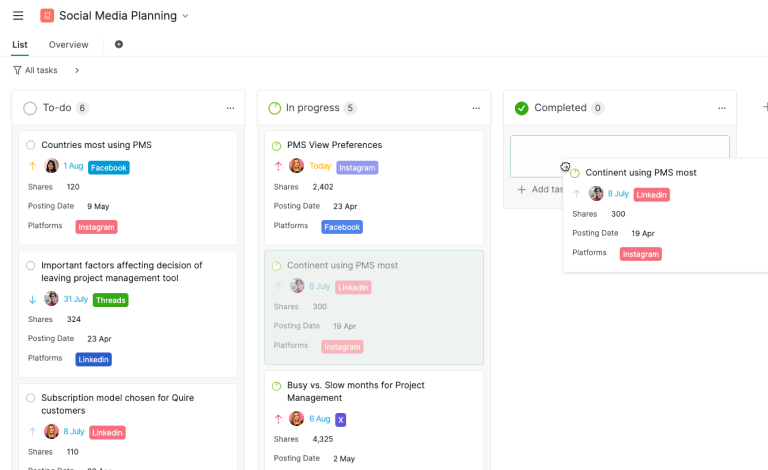
The Project Execution Phase is where the project's plans and strategies are put into action to achieve the project's objectives. During this phase, tasks are assigned and completed, resources are utilized, and deliverables are produced according to the project plan.
Key activities include coordinating team members, managing resources, and ensuring quality standards are met. Continuous communication and collaboration among team members and stakeholders are crucial to address issues and adapt to any changes. The goal of the execution phase is to bring the project plan to life, ensuring that all tasks are completed on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards.
- Task Execution: Perform the tasks and activities outlined in the project plan.
- Resource Management: Manage resources to ensure efficient utilization and address any issues.
- Team Management: Coordinate and support the project team, fostering collaboration and resolving conflicts.
- Stakeholder Communication: Maintain regular communication with stakeholders to provide updates and gather feedback.
- Quality Assurance: Implement quality control measures to ensure deliverables meet the defined standards.
Project Monitoring and Controlling Phase
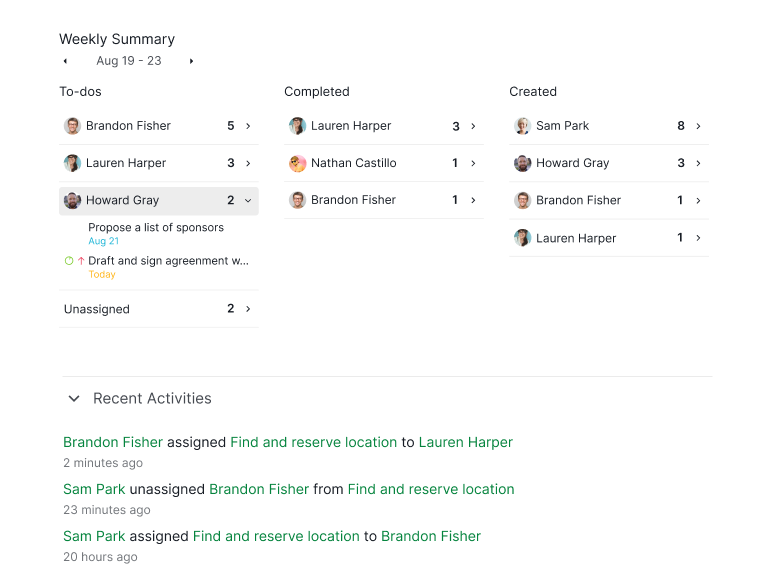
The Project Monitoring and Controlling Phase is an ongoing process that occurs simultaneously with the execution phase, focusing on tracking project performance and making necessary adjustments to ensure successful project delivery. Key activities include measuring progress against the project plan, identifying and managing risks, implementing changes, and maintaining quality control.
This phase involves continuous oversight to detect any deviations from the plan, assess their impact, and take corrective actions to keep the project on track. The goal is to ensure that the project remains aligned with its objectives, timeline, and budget while achieving the desired outcomes.
- Performance Monitoring: Track progress against the project plan, including schedule, budget, and scope.
- Variance Analysis: Identify deviations from the plan and analyze their impact.
- Change Control: Manage changes to the project scope, schedule, or budget through a formal change control process.
- Risk Monitoring: Continuously monitor risks and implement mitigation plans as needed.
- Quality Control: Conduct regular quality checks to ensure deliverables meet the required standards.
Project Closure Phase
The Project Closure Phase is the final stage of the project life cycle, where all project activities are completed, and the project is formally closed. During this phase, the team finalizes all deliverables, obtains stakeholder approvals, and ensures that all project objectives have been met.
Key activities include conducting a final review, documenting lessons learned, releasing project resources, and preparing closure reports. The goal of this phase is to ensure that all project work is concluded satisfactorily, and valuable insights are captured for future projects, marking the formal completion and successful delivery of the project.
- Final Deliverables: Ensure all project deliverables are completed and meet the required standards.
- Project Documentation: Compile and finalize all project documentation, including reports, plans, and records.
- Stakeholder Approval: Obtain formal acceptance of the project deliverables from stakeholders.
- Lessons Learned: Conduct a post-project review to identify lessons learned and best practices for future projects.
- Project Closure Report: Prepare a closure report summarizing the project’s performance, achievements, and any remaining issues.
5 Benefits of Project Life Cycle and its Phases
1. Improved Project Organization:
The structured approach of the project life cycle provides clear guidelines, helping teams stay organized and focused throughout the project. For instance, in a marketing campaign project, the Initiation phase involves defining objectives and scope, the Planning phase involves creating detailed schedules and allocating tasks, the Execution phase sees the team carrying out these tasks, and the Closure phase involves reviewing results and documenting lessons learned.
This structure ensures that all aspects of the campaign are systematically addressed, reducing confusion and enhancing coordination.
2. Enhanced Risk Management:
Each phase of the project life cycle includes risk assessment and mitigation activities, allowing potential issues to be identified and addressed early. For example, in a construction project, the Planning phase might involve identifying risks such as supply chain disruptions or weather delays.
Mitigation strategies, such as securing alternative suppliers or scheduling buffer time, can be put in place. During the Execution phase, continuous monitoring helps identify new risks, and adjustments can be made promptly, ensuring the project stays on track.
3. Better Resource Management:
Detailed planning and execution phases ensure optimal utilization of resources, reducing wastage and improving efficiency. In a software development project, resource management is critical. During the Planning phase, team roles are clearly defined, and resources such as software tools, development environments, and personnel are allocated efficiently.
During Execution, resource utilization is monitored to ensure that developers, testers, and designers are working effectively, leading to timely project completion and reduced costs.
4. Increased Stakeholder Satisfaction:
Regular communication and involvement of stakeholders at each phase ensure their expectations are met and their feedback is incorporated. For instance, in a new product development project, stakeholders such as customers, investors, and senior management are kept informed through regular updates and review meetings.
During the Initiation and Planning phases, their input is sought to align project goals with business objectives. In the Execution phase, their feedback on prototypes or initial deliverables is incorporated, ensuring the final product meets their needs and expectations.
5. Higher Project Success Rate:
By following a systematic approach, projects are more likely to be completed on time, within budget, and to the desired quality standards. For example, in an event planning project, adhering to the project life cycle ensures that every detail, from venue selection to vendor management and guest coordination, is meticulously planned and executed.
The Monitoring and Controlling phase allows for real-time adjustments to address any issues that arise, ensuring the event is successful. The structured approach minimizes the chances of overlooked details or last-minute crises, leading to a higher overall success rate.
These benefits demonstrate how the project life cycle's structured phases—Initiation, Planning, Execution, Monitoring and Controlling, and Closure—can significantly enhance project management, leading to successful project outcomes across various industries.
Project Management Life Cycle with Quire
Quire is a modern project management tool designed to streamline the project life cycle, making it easier for teams to collaborate and manage tasks effectively. Here’s how Quire can enhance each phase of the project life cycle:
1. Initiation Phase:
- Creating Project Charters: Use Quire to create comprehensive project charters that outline the project's objectives, scope, and stakeholders. This ensures that all team members and stakeholders are aligned from the start.
- Defining Objectives: Quire allows you to set clear, measurable objectives and key results (OKRs) for your project, providing a focused direction.
- Real-Time Collaboration: Collaborate with stakeholders in real-time to gather initial requirements, feedback, and approvals. Quire's real-time collaboration features, such as commenting and live updates, ensure everyone is on the same page.
2. Planning Phase:
- Developing Detailed Project Plans: With Quire's intuitive interface, you can create detailed project plans that break down the project into manageable tasks and subtasks. Use nested task lists to outline all necessary steps.
- Allocating Resources: Assign tasks to team members, set deadlines, and allocate resources effectively. Quire's resource management tools help ensure that team members know their responsibilities and deadlines.
- Setting Up Communication Channels: Establish communication channels within Quire to keep the team connected. Use tags, filters, and task comments to streamline discussions and updates.
3. Execution Phase:
- Tracking Task Progress: Monitor the progress of tasks in real-time with Quire's task tracking features. Use visual tools like Kanban boards to see the status of each task at a glance.
- Managing Resources: Keep track of resource utilization and ensure that team members have the necessary support to complete their tasks. Quire's workload view helps in balancing the team's workload.
- Fostering Team Collaboration: Enhance team collaboration with Quire's collaborative features, such as file sharing, task comments, and mentions. This fosters a collaborative environment where team members can work together seamlessly.
4. Monitoring and Controlling Phase:
- Monitoring Project Performance: Use Quire's reporting and analytics tools to monitor project performance against the plan. Track key metrics such as task completion rates, time spent, and progress towards milestones.
- Managing Changes: Handle changes in project scope, timelines, or resources efficiently. Quire allows you to update tasks and plans in real-time, ensuring that the project adapts to any changes promptly.
- Conducting Regular Quality Checks: Schedule and conduct regular quality checks using Quire's task scheduling and reminder features. Document findings and necessary actions directly within the platform.
5. Closure Phase:
- Compiling Final Deliverables: Use Quire to compile and review final deliverables. Ensure that all project requirements have been met and that stakeholders are satisfied with the outcomes.
- Documenting Lessons Learned: Document lessons learned throughout the project in Quire. Create a knowledge base or a final project report that captures successes, challenges, and areas for improvement.
- Preparing Closure Reports: Prepare comprehensive closure reports with Quire's documentation features. Summarize project performance, outcomes, and any recommendations for future projects.
By leveraging Quire's robust project management features, teams can enhance their effectiveness at each phase of the project life cycle, ensuring successful project delivery and continuous improvement.
FAQs for Project Life Cycle
1. What is the purpose of the project life cycle?
The project life cycle provides a structured framework for managing projects, ensuring they are completed efficiently, effectively, and in alignment with stakeholder expectations. This approach breaks down the project into manageable phases, each with specific objectives, deliverables, and milestones. It guides project managers and teams through a systematic process, from the initial concept to the final delivery, facilitating better planning, execution, and control.
2. How do the project phases differ?
Each project phase has distinct objectives and activities that contribute to the project's overall success:
- Initiation: This phase focuses on defining the project's scope, objectives, and feasibility. Key activities include stakeholder identification, project charter development, and initial resource allocation.
- Planning: In this phase, detailed plans are created to guide the project's execution. This includes developing schedules, budgets, risk management plans, and defining roles and responsibilities.
- Execution: The primary focus here is on executing the project plan by completing tasks and deliverables. Activities include coordinating people and resources, managing stakeholder communication, and ensuring quality standards are met.
- Monitoring and Controlling: This ongoing phase involves tracking project performance, measuring progress, and implementing changes as needed to keep the project on track. Key activities include performance reporting, issue resolution, and risk management.
- Closure: The final phase involves completing all project work, obtaining stakeholder approval, and formally closing the project. Activities include final deliverable handover, post-project evaluation, and releasing project resources.
3. Why is the Planning Phase critical?
The Planning Phase is critical because it sets the foundation for the entire project. During this phase, detailed plans are developed that outline the tasks, resources, timelines, and risks involved. Effective planning ensures that all aspects of the project are considered and addressed, reducing the likelihood of issues arising during execution. It also provides a roadmap for the project team, facilitating coordination and communication. Well-defined plans help manage expectations, allocate resources efficiently, and establish a clear path to achieving project objectives.
4. Can the project life cycle be customized?
Yes, the project life cycle can be tailored to fit the specific needs and characteristics of different projects, industries, and organizations. Customization allows for flexibility in addressing unique project requirements, constraints, and stakeholder expectations. For example, a software development project might include iterative phases to accommodate Agile methodologies, while a construction project might follow a more linear approach. By adapting the project life cycle to suit the particular context, organizations can improve project outcomes and better align processes with their strategic goals.
5. How does Quire support the project life cycle?
Quire supports the project life cycle by providing a suite of tools designed to facilitate task management, collaboration, resource allocation, and performance tracking.
With Quire, project teams can create and organize tasks into nested lists, assign responsibilities, and set deadlines. Collaborative features, such as real-time updates and team communication tools, enhance coordination and ensure everyone stays informed.
Resource management capabilities help allocate and track the use of resources effectively, while performance metrics and reporting tools enable continuous monitoring and adjustment.
By integrating these features, Quire makes it easier to manage projects from initiation to closure, ensuring they are completed successfully.
In conclusion, understanding and implementing the project life cycle is essential for successful project management. By following the five phases and leveraging tools like Quire, project teams can enhance efficiency, manage risks, and achieve their project goals effectively.


