project management · Jul 26, 2024
What is a Kanban Card? Guide, Benefits, and Examples

Feeling overwhelmed by project chaos? Staying organized and efficient is crucial in today's fast-paced world. Enter the Kanban card, a simple yet powerful tool that's surging in popularity.
This blog post will be your one-stop guide to Kanban cards. We'll cover everything you need to know: what they are, where they came from, why they're awesome, and how to use them (including digital versions!).
What is a Kanban Card?
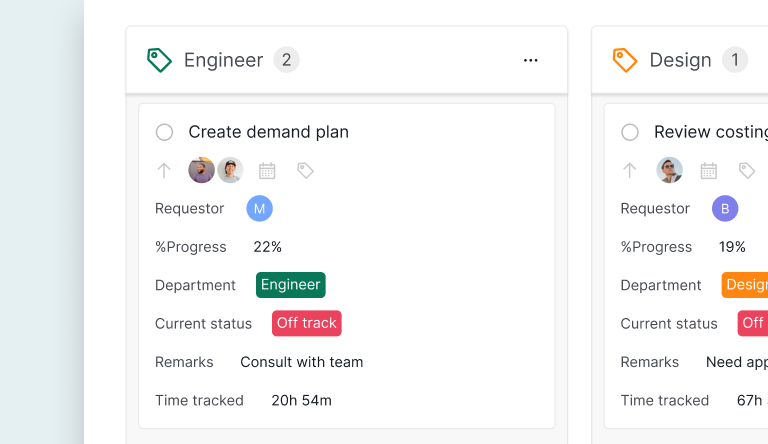
A Kanban card is a visual representation of a task or work item in a Kanban system, a method used to visualize and manage workflow. Each card typically contains essential details about a task, such as its description, status, assignee, and deadline. The cards are placed on a Kanban board, which is divided into columns representing different stages of the workflow, such as "To Do," "In Progress," and "Done."
The visual nature of Kanban cards helps teams to quickly understand what tasks need to be done, who is responsible for them, and their current status. This transparency facilitates better communication and collaboration within the team.
The Origin of Kanban Card
The concept of the Kanban card originates from the Japanese manufacturing industry, specifically from Toyota's production system in the 1940s. The term "Kanban" itself means "signboard" or "billboard" in Japanese. The system was developed by Taiichi Ohno, an industrial engineer at Toyota, to improve manufacturing efficiency and reduce waste.
In the Toyota Production System, Kanban cards were used as visual signals to indicate the need to move materials within the production process. When a particular part or material was needed, a Kanban card would be sent upstream, prompting the production of more units. This just-in-time (JIT) approach ensured that inventory levels were kept to a minimum and production was closely aligned with demand.
Over time, the principles of the Kanban system have been adapted for use in various industries beyond manufacturing, including software development, marketing, and project management.
5 Benefits of Using Kanban Card
- Improved Visibility: Imagine a software development team working on a new product release. By using Kanban cards on a digital board, each task (such as coding, testing, and reviewing) is visually represented. Team members can easily see which tasks are in progress, which are pending, and which are completed. This visual clarity helps in quickly identifying bottlenecks, such as a task stuck in the testing phase, allowing the team to address the issue promptly and maintain steady progress.
- Enhanced Communication: Consider a marketing team planning a new campaign. With Kanban cards, they can visualize each step of the campaign, from brainstorming ideas to executing social media posts. Team members can instantly see who is responsible for each task and the current status, reducing the need for constant check-ins and long meetings. For example, if a content writer sees that the design team has completed the graphics, they can immediately start integrating them into their posts, streamlining the workflow.
- Increased Efficiency: Take a customer support team that handles various service tickets for instance. Using Kanban cards, they can prioritize tickets based on urgency and complexity, ensuring that the most critical issues are addressed first. This system minimizes idle time as support agents always know what the next task is. As a result, tickets are resolved faster, and customer satisfaction improves due to quicker response times.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Imagine a startup that initially uses Kanban cards to manage a small team of five people working on product development. As the company grows, it can scale the system to include more departments, such as marketing and sales. The Kanban board can be expanded to accommodate the increasing number of tasks and team members, making it a versatile tool for both small and large-scale projects.
- Continuous Improvement: Picture a manufacturing team aiming to enhance their production process. By using Kanban cards to track each step of the production line, they can regularly review and analyze their workflow. If they notice that a particular stage consistently causes delays, they can brainstorm and implement solutions, such as reallocating resources or adjusting timelines. Over time, these incremental improvements lead to a more efficient and effective production process.
The Purpose of the Kanban Card
The primary purpose of a Kanban card is to provide a clear, visual representation of a task and its status within a workflow. This visualization helps teams to manage their work more effectively by:
- Tracking Progress: Kanban cards allow teams to track the progress of tasks from start to finish. By moving cards across columns on a Kanban board, team members can easily see what has been completed and what is still in progress.
- Identifying Bottlenecks: By visualizing the workflow, teams can quickly identify bottlenecks or areas where tasks are getting stuck. This enables them to address issues promptly and keep work flowing smoothly.
- Prioritizing Tasks: Kanban cards help teams prioritize tasks and ensure that the most important work is being done first. By organizing cards in order of priority, teams can focus on high-impact activities and deliver value more quickly.
- Promoting Accountability: Assigning tasks to specific team members using Kanban cards promotes accountability and ensures that everyone knows their responsibilities. This clarity helps to prevent confusion and ensures that tasks are completed efficiently.
5 Kanban Card Examples
Basic Task Card: A simple Kanban card might include the task name, description, assignee, and due date. For example, a card titled "Write Blog Post" could have details like "Create a 1000-word blog post on Kanban cards," assigned to "John," with a due date of "June 20, 2024."
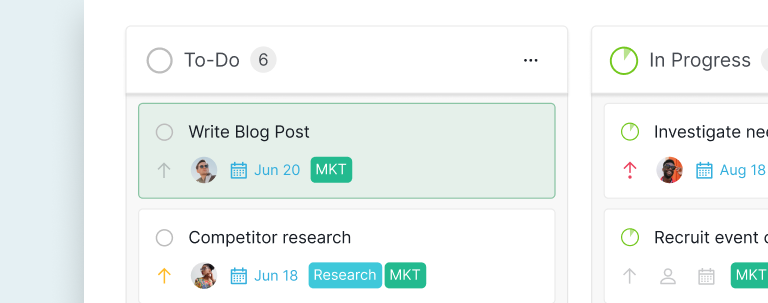
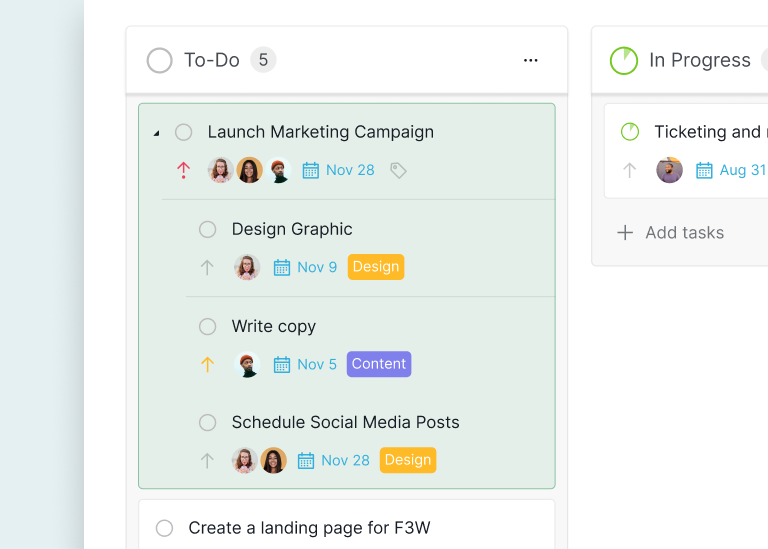
Subtask Card: For more complex tasks, a Kanban card might include a checklist of subtasks. For example, a card for "Launch Marketing Campaign" could have subtasks like "Design Graphics," "Write Copy," "Set Up Landing Page," and "Schedule Social Media Posts."
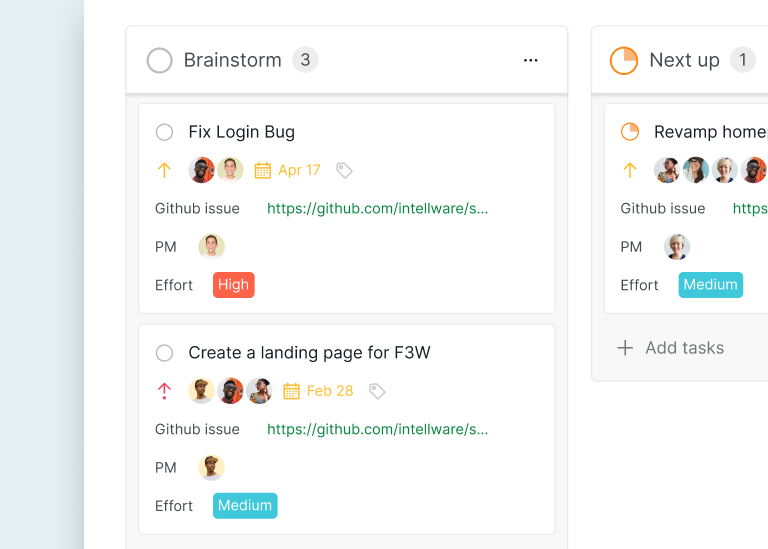
Bug Tracking Card: In software development, Kanban cards can be used to track bugs. A card might include details like the bug description, steps to reproduce, severity, and assigned developer. For instance, a card titled "Fix Login Bug" could include "Users unable to log in with Google," assigned to "Sarah," with a severity level of "High."
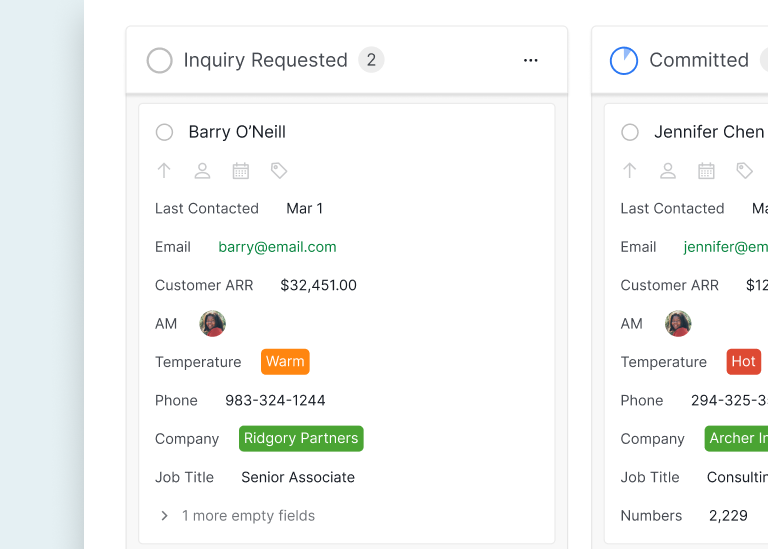
User Story Card: In Agile development, user stories are often represented as Kanban cards. A card might include the user story, acceptance criteria, and priority. For example, a card titled "Jennifer Chen" could include the user information and profile. The card can include the Customer ARR and the current status as well as the temperature of the customer.
Feedback Card: Kanban cards can also be used to track customer feedback. A card might include the feedback description, customer name, and any follow-up actions. For instance, a card titled "Customer Feedback on UI" could include "Customer mentioned the interface is not intuitive," with follow-up actions like "Schedule a meeting with the design team."
What Can a Team Use Digital Kanban Cards For?
Digital Kanban cards offer additional features and functionalities compared to their physical counterparts, making them even more versatile for modern teams. Here are some common uses:
- Task Management: Digital Kanban cards are used to manage and track tasks within a project. Teams can create, assign, and move cards through different stages of the workflow, ensuring that work is organized and progressing smoothly.
- Collaboration: Digital Kanban cards facilitate collaboration by allowing team members to comment on tasks, attach files, and provide updates in real-time. This centralizes communication and ensures that everyone is on the same page.
- Reporting and Analytics: Many digital Kanban tools offer reporting and analytics features, providing insights into team performance, workflow efficiency, and project progress. These insights can help teams to identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions.
- Integration with Other Tools: Digital Kanban cards can often be integrated with other project management and productivity tools, such as time-tracking software, communication platforms, and calendars. This integration streamlines workflows and reduces the need for manual data entry.
- Remote Work: In today's increasingly remote work environment, digital Kanban cards are essential for maintaining team cohesion and productivity. They enable distributed teams to collaborate effectively, regardless of location.
3 Steps to Start with Quire Kanban Cards
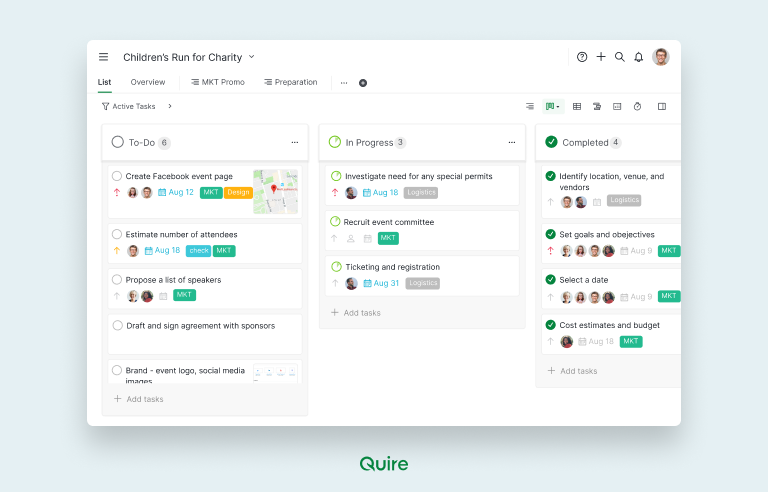
Quire is a popular project management tool that incorporates Kanban boards. Here’s how you can get started with Quire Kanban cards:
- Set Up Your Project: Create a new project in Quire and set up your Kanban board. Define the columns that represent different stages of your workflow, such as "To Do," "In Progress," and "Done."
- Create and Customize Kanban Cards: Add tasks to your Kanban board by creating Kanban cards. Customize each card with relevant details, such as task descriptions, assignees, due dates, and any necessary checklists or attachments.
- Manage and Track Progress: Use your Kanban board to manage and track the progress of tasks. Move cards across columns as work progresses, and use Quire’s features to collaborate with team members, track deadlines, and monitor overall project progress.
By following these steps, you can harness the power of Quire Kanban cards to improve your team’s productivity, communication, and project management efficiency.
In conclusion, Kanban cards are a powerful tool for visualizing and managing workflow. Whether used in physical form or through digital platforms like Quire, they offer numerous benefits that can help teams to work more efficiently and effectively. By understanding the origins, benefits, and practical applications of Kanban cards, you can leverage this system to enhance your project management practices and drive continuous improvement within your team.


